In today’s digital age, cloud computing has become an indispensable part of modern business operations. Cloud technology offers scalability, flexibility, cost-efficiency, and accessibility that traditional on-premises infrastructure cannot match. As organizations continue to migrate their workloads to the cloud, two prominent cloud deployment models have emerged: multi-cloud vs hybrid cloud. In this article, we will explore these two cloud strategies, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose the right approach for your business.
Understanding Cloud Deployment Models
Before delving into the multi-cloud vs. hybrid cloud debate, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of these two deployment models.
Multi-Cloud
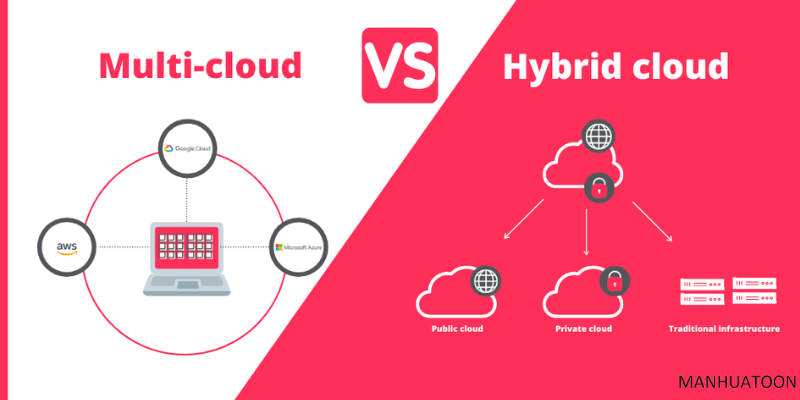
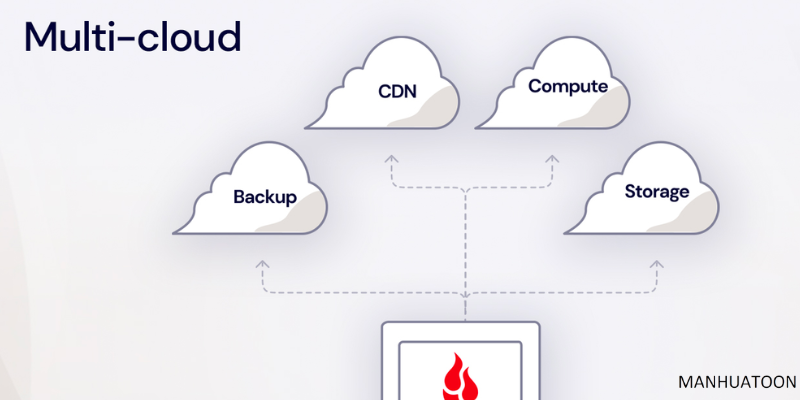
Multi-cloud is a cloud strategy where an organization uses multiple cloud service providers to host its applications and data. This approach allows businesses to distribute workloads across different cloud platforms, reducing vendor lock-in and enhancing resilience. Each cloud provider is typically chosen based on its specific strengths and capabilities for particular tasks or applications.
Key features of multi-cloud include:
- Vendor Diversity: Using multiple cloud providers reduces dependence on a single vendor, mitigating risks associated with service outages or changes in pricing and policies.
- Optimized Workloads: Applications and workloads can be placed on the most suitable cloud platform based on performance, cost, and compliance requirements.
- Geographical Distribution: Multi-cloud enables organizations to deploy resources in different regions or data centers, improving global availability and reducing latency.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud is a cloud strategy that combines on-premises infrastructure (private cloud) with one or more public cloud providers. This approach offers a balance between the control of on-premises resources and the scalability of public cloud services. Hybrid cloud solutions often involve integrating and orchestrating data and applications between the private and public cloud environments.
Key features of hybrid cloud include:
- Data and Application Portability: Data and applications can move seamlessly between on-premises and public cloud environments, providing flexibility and scalability.
- Resource Optimization: Businesses can scale resources up or down as needed, leveraging the public cloud’s elasticity while maintaining critical workloads on-premises.
- Security and Compliance: Sensitive data can be kept on the private cloud to meet regulatory requirements, while less-sensitive workloads can run in the public cloud.
Now that we have a clear understanding of these two cloud deployment models, let’s explore the multi-cloud vs. hybrid cloud comparison in more detail.
Multi-Cloud: Pros and Cons
Pros of Multi-Cloud
- Resilience and Redundancy: Multi-cloud enhances fault tolerance by spreading workloads across different providers. If one provider experiences an outage, applications and data can seamlessly failover to another.
- Best-of-Breed Services: Organizations can select the most appropriate cloud provider for each specific service or workload, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency.
- Competitive Pricing: Multi-cloud can enable cost optimization by taking advantage of competitive pricing, discounts, and promotions offered by various providers.
- Compliance and Data Sovereignty: Businesses can ensure data sovereignty and compliance by selecting cloud regions or providers that meet specific regulatory requirements.
- Avoiding Vendor Lock-In: Multi-cloud reduces the risk of vendor lock-in, as organizations are not tied to a single provider’s ecosystem.
Cons of Multi-Cloud
- Complexity: Managing multiple cloud providers can be complex and require specialized expertise. It may involve dealing with different APIs, billing models, and management tools.
- Increased Costs: Without careful management, the complexity of multi-cloud can lead to higher operational and management costs.
- Data Integration Challenges: Integrating data and applications across multiple cloud environments can be challenging, requiring robust networking and integration solutions.
- Security Risks: Security can be more challenging to maintain in a multi-cloud environment due to the diversity of providers and potential security gaps.
Hybrid Cloud: Pros and Cons
Pros of Hybrid Cloud
- Flexibility: Hybrid cloud provides the flexibility to scale resources on-demand, utilizing public cloud resources when needed while maintaining control over critical workloads on-premises.
- Data Control: Sensitive data can be kept on a private cloud, giving organizations greater control over security and compliance.
- Cost Savings: Hybrid cloud can lead to cost savings by optimizing resource allocation and avoiding unnecessary public cloud expenses.
- Legacy System Integration: Organizations with existing on-premises infrastructure can smoothly integrate their legacy systems with cloud services.
Cons of Hybrid Cloud
- Complexity: Managing the integration between on-premises and cloud environments can be complex, requiring careful planning and execution.
- Limited Public Cloud Benefits: Organizations may not fully benefit from the agility and scalability of public cloud services for certain workloads.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring consistent security and compliance policies across both on-premises and public cloud environments can be challenging.
- Costs of Data Transfer: Moving data between on-premises and the public cloud can incur data transfer costs, which should be considered in the budget.
Choosing the Right Cloud Strategy
The decision between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud should align with your organization’s specific goals, requirements, and resources. Here are some factors to consider when making this decision:
1. Workload Characteristics
Examine your workloads and applications to determine their suitability for each cloud model. Some applications may benefit from the flexibility of multi-cloud, while others may require the data control and security of a hybrid cloud.
2. Data Sensitivity and Compliance
Consider the nature of your data and any regulatory compliance requirements. If you handle highly sensitive data, a hybrid cloud with on-premises control might be the best choice. If data sovereignty is a concern, multi-cloud can offer options for data residency.
3. Resource Scalability
Assess your scalability needs. If your organization requires the ability to rapidly scale resources up or down, a multi-cloud approach might be more suitable. If resource requirements are relatively stable, a hybrid cloud could offer cost savings.
4. IT Expertise
Evaluate your IT team’s skills and expertise. Managing a multi-cloud environment can be complex and may require specialized knowledge, while a hybrid cloud might be more manageable with existing skill sets.
5. Budget Constraints
Consider your budget and the total cost of ownership. While multi-cloud can offer competitive pricing opportunities, it can also lead to increased operational costs if not managed effectively. A hybrid cloud may provide better cost control in certain scenarios.
6. Long-Term Strategy
Think about your organization’s long-term cloud strategy. Is your goal to gradually migrate to the cloud while maintaining existing infrastructure, or do you intend to maintain a multi-cloud strategy for the foreseeable future?
Conclusion
Choosing between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud is a critical decision that can significantly impact your organization’s agility, scalability, security, and cost efficiency. There is no one-size-fits-all answer, and the right choice depends on your unique business requirements.
In many cases, organizations opt for a hybrid cloud strategy to strike a balance between control and flexibility. However, multi-cloud can be a viable choice for businesses seeking to harness the strengths of different cloud providers and mitigate risks associated with vendor lock-in.
Ultimately, a well-informed decision, based on a thorough assessment of your workloads, data, IT capabilities, and long-term goals, will ensure that your cloud strategy
